The term AI Agent has overtaken chatbots in popularity. Chatbot companies transformed into AI Agent companies seemingly overnight. Is this just a marketing exercise or is there some value in using a different term? This article explores how we got here.
In the past 2 years the term “AI Agent” has taken hold and managed to surpass, in popularity, the term chatbot. Given the overall interest in chatbots that kicked off with the release of ChatGPT, that is quite a feat.
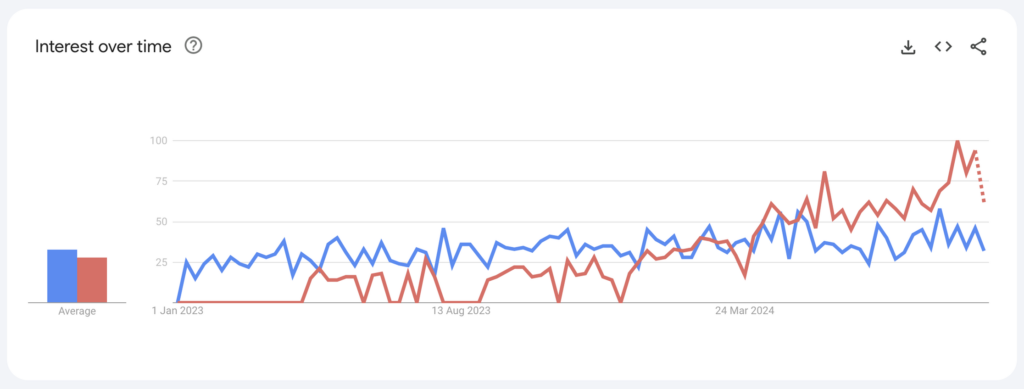
Google Trends for Chatbots and AI Agents since 2023
However, in a space that is relentless in the constant update and creation of new terminology, it also adds further confusion. Organizations were just wrapping their heads around chatbots and now they have to deal with AI Agents. Should they still be thinking of chatbots or are AI Agents where it’s at, and how are these things even different?
In the next few paragraphs we will explore how we got here, what are AI Agents (and more specifically Conversational AI Agents), discuss what you can achieve with them today and talk about what is required to design, develop, maintain and scale them.
How we got here
Chatbots were supposed to be the future
In many ways, 2016, was the year that conversational AI started to seriously be considered as an enterprise technology. OpenAI was just a year old, Amazon Alexa had just become widely available as a platform, Facebook launched Messenger Bots and Satya Nadella, Microsoft CEO, was declaring that chatbots would replace apps. Just a year later, Google published the seminal academic paper “Attention is all you need” describing the architecture that is at the heart of today’s large language models. It seemed that conversational AI was about to take over the world, but, as ever with innovation, it faced several hurdles. The most significant hurdle was that it took a lot of hard work with large teams to get to chatbots that were useful and reliable. It was a dive into the unknown that very few organizations could afford or were willing to take.
LLMs take over
Fast forward to 2024 and much progress has been made. The core technological capability required is now generations ahead. Large Language Models have taken over and they can perform the challenging natural language understanding and reasoning tasks required of them to power solutions.
This created a seismic shift in the Conversational AI space. In 2022 practitioners were finally coalescing around a specific, widely understood set of NLU techniques for designing and developing chatbots. Then, seemingly overnight all of that was upended as Large Language Models took the stage. Conversation designers morphed into prompt engineers, and literally 1000s of hours of development into language classification became obsolete.
As with the advent of any general-purpose technology, LLMs can replace countless tasks that previously required specialized systems. The one saving grace of the old guard was that in 2022 LLM costs were still prohibitive and concerns around safety were much more profound. In 2024, however, costs have gone down orders of magnitude, speed has increased and there is a rich ecosystem of LLMs and techniques to cater for different needs.
The ways we develop Conversational AI solutions today and the capabilities that are available are so significant that new terms and new communities have evolved around those terms (often absorbing the old communities that formed around chatbots).
What are Conversational AI Agents?
This is where Conversational AI agents come in.
Conversational AI Agents are software applications whose main mode of interaction (but not the only one) is natural language. They converse with a user to help achieve a specific goal and combine different application interface components (anything from a simple button to more complex forms, maps, eSign, payment, etc) to help a person achieve that goal. So far not that different from a “traditional” chatbot you might say. So are these just the same thing with a new and improved name to help marketing departments?
Well, let’s not fool ourselves. The needs of marketing and rebranding are always part of the story. In their simplest form, Conversational AI Agents are just better chatbots! There is, however, a fundamental technological leap forward that justifies a new moniker and a different way of looking at the technology.
The main difference between a chatbot and a Conversational AI agent is that an agent has far more powerful “reasoning”, “acting” and “sensing” capabilities that make use, mostly, of LLMs. A Conversational AI Agent is given instructions in natural language and will make use of LLMs to interpret those instructions and determine the next actions.
A Conversational AI Agent is essentially a network of prompts (instructions in natural language) that processes information and makes decisions, connected through an overall execution engine that orchestrates the various instructions towards a specific goal.
Much more could be said here but for the purposes of this article, I will provide a summary of a few more capabilities. Not all Conversational AI agents need all of these, but these are some of the things I would expect to see in Enterprise Conversational AI Agents that make them more interesting than traditional chatbots and make them useful tools to have.
Conversational AI agents:
- Can work towards a specific goal or goals relevant to your organization based on natural language instructions
- Learn and use information from the documents and data you supply
- Distinguish between knowledge they can confidently use and other information they should not be using
- Integrate into your systems via APIs and use that information to drive further action
- Adapt to user needs in real time
- Follow complex, multi-step, processes over period of time
- Ensure organizational rules and regulations are adhered to
- Collect insights about what users need and how the solution as a whole is performing
What can you do with a Conversational AI Agent?
Currently, the most common application of conversational AI is customer support, where a Conversational AI Agent can answer questions and provide information, there is so much more you can do.
Here are just three scenarios where Conversational AI agents can provide value today.
Accompany users through complex, multi-step processes
Conversational AI agents can help users navigate and complete complex tasks such as buying health insurance, making an insurance claim, booking an event at a hotel, submitting a mortgage application, moving home and setting up utilities. These processes combine multiple steps, often contain complex jargon and are daunting to face for users. A Conversational AI Agent can act as a helpful co-pilot to complete these complex processes and help users get over any unexpected hurdles. This enables an improved user experience while increasing online sale conversion and reducing operational costs.
Personalized recommendations and decision support
Conversational AI Agents can assist users in navigating product catalogs and provide personalized recommendations. This can be particularly valuable where products can have an extensive bill of materials, and complex configurations or require some domain expertise. A Conversational AI agent can combine the organization’s knowledge with a broad understanding of user needs, to drive better customer experience, increase basket sizes, improve online sale conversion and reduce the need for costly pre-sales assistance before a customer can make a choice.
Education and training
Conversational AI Agents are exceptionally well-suited to assist in education and training – allowing a user to explore a subject, ask questions and provide immediate feedback on the answers, adjusting lesson plans and next steps based on the user’s specific needs.
What are the hurdles to the adoption of Conversational AI Agents?
Now, if Conversational AI Agents offer so many possibilities for automation and improved user experience how come they are not what every single organization is focussing on building?
At OpenDialog we talk with organizations looking to do this every day and we can see three main hurdles.
- Concerns about safety and reliability of outcome, adherence to rules and regulations, especially when the AI agent is interacting directly with customers
- Fear that there is a high upfront cost to develop a solution and significant ongoing costs to maintain it
- Lack of skills internal to the organization on how to develop Conversational AI Agents and correctly harness the raw capabilities of large language models to effectively use them to deliver a specific outcome.
How OpenDialog makes Conversational AI agents possible
Now, unsurprisingly, at OpenDialog our goal is to bring Conversational AI Agents within the reach of every organization and do so through a framework that allows you to move quickly, safely and reliably without needing to have teams with deep AI skills.
We’ve designed OpenDialog to be The “WordPress” for Conversational AI Agents & Co-Pilots—a no-code, enterprise-grade design and management platform that makes it possible for organizations to design their Conversational AI agents quickly, safely and efficiently while being able to maintain and scale them over time overcoming the hurdles mentioned above.
The OpenDialog methodology makes it easy for new entrants to the field of Conversational AI Agents to develop sophisticated solutions quickly. Applications built in the OpenDialog way are easier to understand, easier to maintain and more predictable in their behaviour, reducing the overall design effort significantly.
The way we achieve this is threefold.
A consistent method that promotes safety
First, we provide a streamlined way of designing Conversational AI Agents that is tightly integrated with LLMs and with the ability to define explicit rules. This means you find a ready-made path to follow that will deliver consistent and reliable results, pulling in LLM capability as required and only when required, and leads to solutions that are reusable.
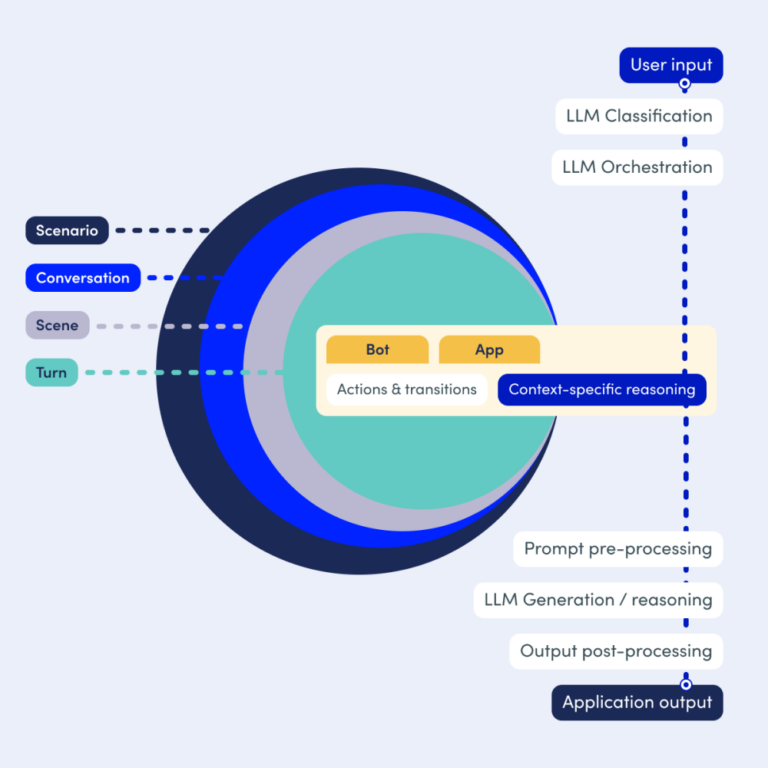
The OpenDialog Framework
An integrated Platform
Second, we provide a single integrated platform, through which you can design, develop, integrate, test and maintain your agents. This means you will find all the functionality there from our AI Agent orchestration engine, prompt management, RAG to our rich Web-based UI frontend with multiple widgets for you to use and deep analytics.
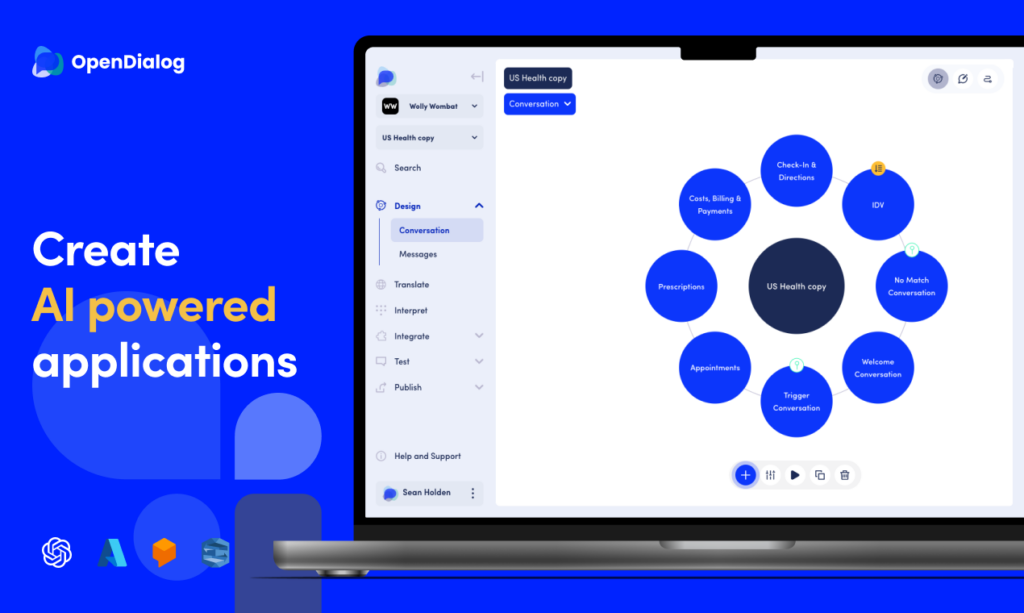
OpenDialog provides everything you need to develop a Conversational AI Agent
A scalable, future, proof solution
Third, we future-proof your solutions by providing a layer through which you can consistently access LLM capability. We realize that the space is in constant evolution and you need to be able to use the LLMs that will best suite your needs and be able to upgrade your agents to take advantage of new capabilities without having to redesign the whole thing.
At the same time, the OpenDialog platform provides all the features required for an enterprise-grade Gen AI application, freeing up your developers to focus on developing the best possible solution and integration for your needs without having to worry about the complexities of running a GenAI tech stack.
Conclusion
Conversational AI Agents represent the next frontier in business automation, providing organizations with the ability to offer personalized, efficient, and reliable interactions with their customers, employees and partners. It is not just a marketing gimmick but an acknowledgement that the technology has matured considerably and can support whole new areas of application. From automating complex, labor intensive processes to offering tailored recommendations and enhancing training experiences, the potential of these agents is considerable.
However, concerns about safety, cost, and the technical skills required to implement these solutions still hinders their adoption.
OpenDialog addresses these challenges by offering a powerful platform that combines ease of use with enterprise-grade features, ensuring businesses can quickly design, maintain, and scale safe ConversationalAI Agents with confidence.
To find out more about OpenDialog check out our documentation.